Yanka Kupala
State University of Grodno
Super User
The Faculty of Law of Yanka Kupala State University of Grodno held an online event “Welcome Day”

"Welcome Day" is an online event organized by the Faculty of Law with the aim of presenting our university to the Republic of Uzbekistan. The meeting was attended by representatives of universities, colleges of law and technical schools of Uzbekistan.
The Faculty of Law held an online event “Welcome Day” with educational institutions of the Republic of Uzbekistan. Tashkent State University of Law, Tashkent College of Law, and other colleges of law from different cities of Uzbekistan joined the online event. About 20 Uzbek educational institutions took part in the “Welcome Day” event.
Svetlana Cheburanova, the Dean of the Faculty of Law, addressed to the participants of the online event with a welcome speech, shared the details about studying at Yanka Kupala State University of Grodno at the Faculty of Law. She answered questions that followed from employees and students of Uzbek colleges of law. Most of the questions concerned the specifics of obtaining a dual degree, internship, tuition fees, terms of admission, living conditions for foreign students, and further possibilities of studying for a master's degree.
Two videos were presented at the event: an introductory video about Yanka Kupala State University of Grodno and a video about the Faculty of Law.
Сitizens of Uzbekistan, 2nd year students of the Faculty of Law majoring in “International Law” made a presentation “I study at Yanka Kupala State University of Grodno”. Students shared their impressions of YKSUG, studying at the Faculty of Law, highlighted the active scientific life of students and the opportunity to participate in various international conferences.
With great interest, they presented the activities of the Foreign Students Association aimed to popularize the national culture and traditions of foreign students. They also told about the living conditions in the dormitory vividly and with interest. Students noted the beauty of Grodno, the kindness of Grodno residents, the beautiful nature of Belarus. Their performance was accompanied by a display of personal photos.
At the end of the “Welcome Day”, the representatives of Uzbekistan thanked for the online event, noting its informativeness and usefulness.


Professor from School of Journalism and Mass Communication of Saint Petersburg State University Lilia Duskaeva gave a course of lectures in Yanka Kupala State University of Grodno
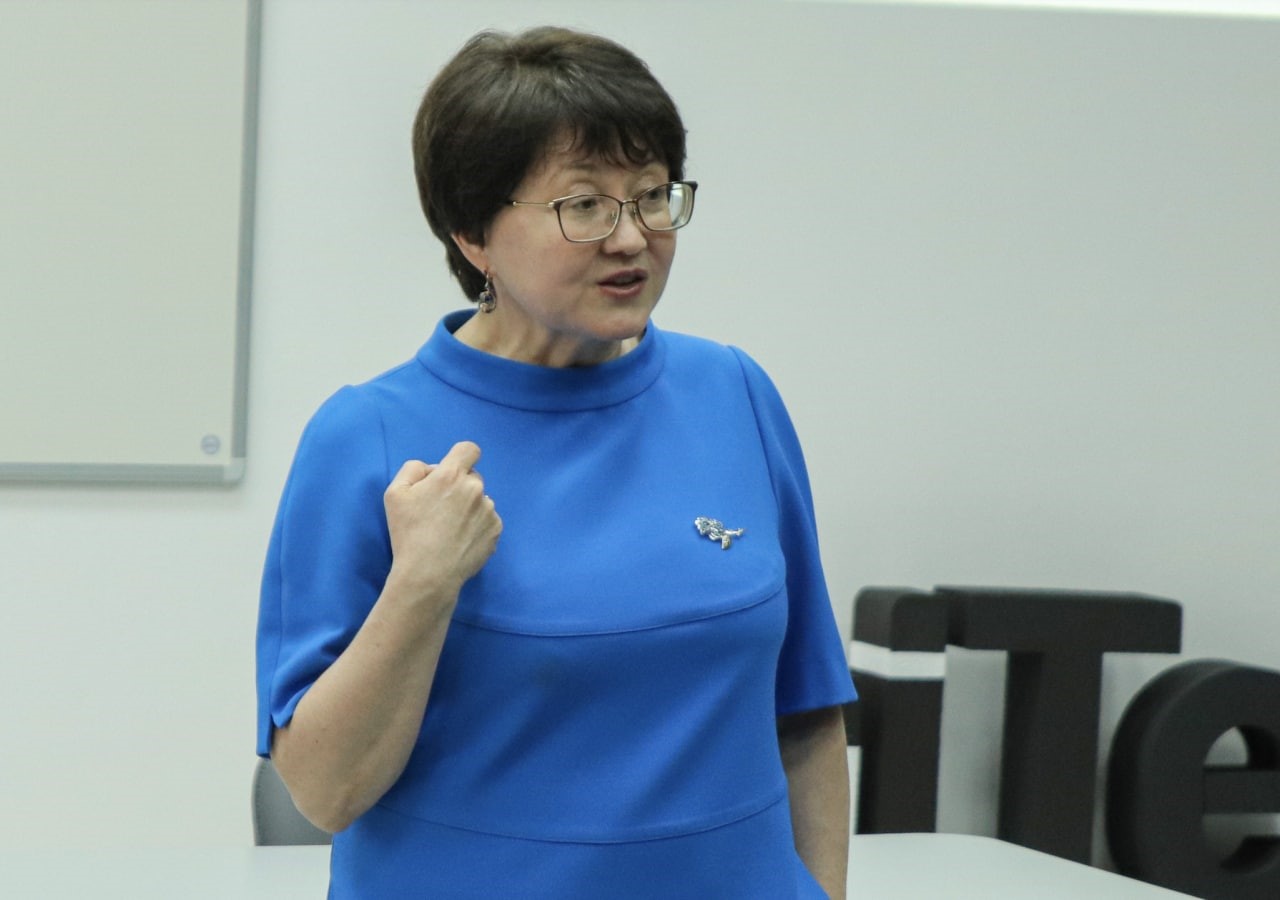

“Language and style of Mass Communication” course of lectures on the disciplines “Journalism” and “Information and Communication” for students of the 2nd year took place in Yanka Kupala State University of Grodno. Doctor of Philology, Professor and Head of the Media Linguistics Department of Saint Petersburg State University Lilia Duskaeva gave lectures in 4-6 May. During this period of time students, future journalists and information and communication specialists got to learn about the Professor’s method of media text analysis.
Journalism Department of the Faculty of History, Communication and Tourism of Yanka Kupala State University and Media Linguistics Department of Saint Petersburg State University established close cooperation over the previous years. Lilia Duskaeva and other teachers from Saint Petersburg State University regularly attend scientific events in Yanka Kupala State University. Cooperative work between the universities led to a few scientific publications connected with the media text analysis including Speech Etiquette in Slavic Online Communities monograph.
Head of the Journalism Department Inna Minchuk and senior lecturers Tamara Pivovarchik and Iryna Gerasimchik were invited as members of the Belarusian National Subcommittee of the Media Linguistics Committee.

Yanka Kupala State University of Grodno was included to THE University Impact Rankings 2022 for the first time

THE University Impact Rankings is one of the largest researches of THE Ranking (Times Higher Education). It has been functioning since 2019, focusing mainly on the world universities’ achievements of the goals of UN in sustainable development sphere.
In 2022 Impact Rankings 1406 universities of 106 countries, including 6 Belarusian universities, appeared in the rank.
More information can be found on Times Higher Education site.
Learn about Yanka Kupala State University in World Rankings here.
Professor from Yanka Kupala State University participated as an expert in the International competition of student’s research works “Digital Discovery”
XII Eurasian Economic Youth Forum “Russia and the World in New Realities: Changing in World Economic Relations” took place in April 26-29 in the Ural State University of Economics. During the forum the competition of the research works “Digital Discovery” was held. Igor Martynenko, Doctor of Law, Professor and Head of the Civil Law and Procedure Department, was invited as an expert from Yanka Kupala State University.
The event included 45 competitions and 6 congresses, public lectures, plenary meeting and meeting of students and diplomats. This year more than 8000 participants from 92 countries and 76 regions in Russia took part in the forum. Students and young professionals presented the results of their research and encouraged the listeners from different countries to study and make researches too.
During his speech Igor Martynenko paid attention to the necessity of exchange in knowledge, ideas and experience of using legal regulatory mechanisms in economic processes. He also shared the achievements of Belarus in this field.
The Organizing Committee of the Eurasian Economic Youth Forum commended the Professor’s participation in the international event. He received a Letter of Gratitude from Yakov Silin, Rector of the Ural State University of Economics.

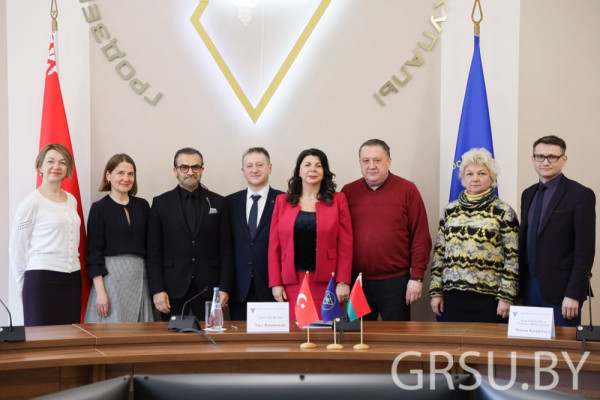
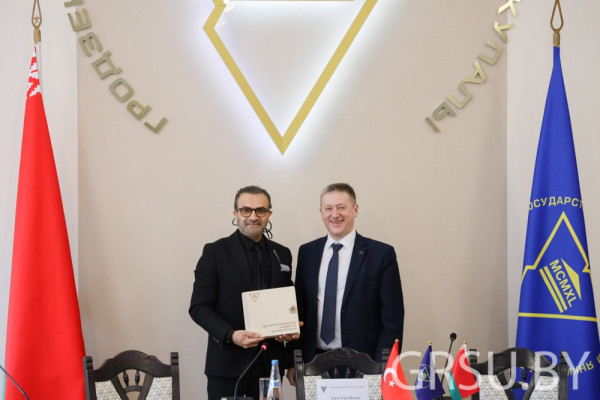
A visiting professor from Turkey will give lectures at Yanka Kupala State University of Grodno
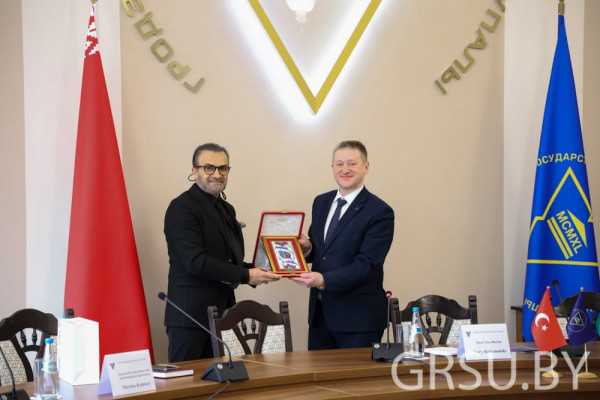

For four days, Candidate of Mathematical Sciences, Associate Professor, Dean of the Business School, Head of the Distance Learning Center of Istanbul Medipol University Gökhan Silahtaroğlu will give lectures to our students and get acquainted with the potential of Yanka Kupala State University of Grodno.
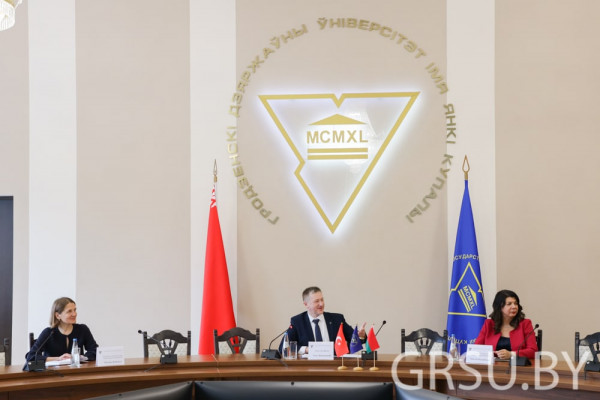
The working visit was opened by a meeting of Gokhan Silakhtaroglu and First Vice-Rector of Yanka Kupala State University of Grodno Yury Ramanouski, which was also attended by Maryna Karpitskaya, Dean of the Faculty of Economics and Management, Yury Hniazdouski, Dean of the Faculty of Pedagogy, Alena Livak, Dean of the Faculty of Mathematics and Information Scienсe, Aleksandr Vorontsov, Dean of the Faculty of Innovative Mechanic Engineering, Marina Kolotsey, Head of the educational and methodological department, Volha Minava, Head of the Department for International Relations, Volha Piarkova, Senior Lecturer of the Department of Foreign languages, interpreter.
The participants of the meeting discussed the work of faculties and structural units and expressed hope for close cooperation.
The visiting professor will give lectures on the following topics «Network Security Problems» (discipline «Fundamentals of network technologies»), «Fundamentals of project management» (discipline «Computer Information Technology»). He will also conduct seminars and laboratory classes.
The visit takes place within the framework of the «Visiting Professor» program, and the Faculty of Economics and Management became the host.
A visiting professor from Turkey will give lectures at Yanka Kupala State University of Grodno

For four days, Candidate of Mathematical Sciences, Associate Professor, Dean of the Business School, Head of the Distance Learning Center of Istanbul Medipol University Gökhan Silahtaroğlu will give lectures to our students and get acquainted with the potential of Yanka Kupala State University of Grodno.
The working visit was opened by a meeting of Gokhan Silakhtaroglu and First Vice-Rector of Yanka Kupala State University of Grodno Yury Ramanouski, which was also attended by Maryna Karpitskaya, Dean of the Faculty of Economics and Management, Yury Hniazdouski, Dean of the Faculty of Pedagogy, Alena Livak, Dean of the Faculty of Mathematics and Information Scienсe, Aleksandr Vorontsov, Dean of the Faculty of Innovative Mechanic Engineering, Marina Kolotsey, Head of the educational and methodological department, Volha Minava, Head of the Department for International Relations, Volha Piarkova, Senior Lecturer of the Department of Foreign languages, interpreter.
The participants of the meeting discussed the work of faculties and structural units and expressed hope for close cooperation.
The visiting professor will give lectures on the following topics «Network Security Problems» (discipline «Fundamentals of network technologies»), «Fundamentals of project management» (discipline «Computer Information Technology»). He will also conduct seminars and laboratory classes.
The visit takes place within the framework of the «Visiting Professor» program, and the Faculty of Economics and Management became the host.
Joint education programs:
|
№ |
Name of the Partner University or program |
Country |
Duration of studies |
Contract number and date of conclusion |
Faculty / Speciality |
Language of study |
Form of education |
Documents on education |
|
1 |
Kokand State University |
Republic of Uzbekistan |
4 years (2+2) |
16.1-25/21-17 07.05.2021 |
Faculty of Psychology / Practical Psychology |
Russian |
Full-time |
Diploma of Higher Education in Yanka Kupala State University of Grodno and diploma of higher education in Kokand State University |
|
2 |
Kokand State University |
Republic of Uzbekistan |
4 years (2+2) |
16.1-25/23-29 19.06.2023 |
Faculty of Psychology / Psychology |
Russian |
Full-time |
Diploma of Higher Education in Yanka Kupala State University of Grodno and diploma of higher education in Kokand State University |
|
3 |
Kokand State University |
Republic of Uzbekistan |
2 years (1+1) |
16.1-25/24-25 10.06.2024 |
Faculty of Psychology / Psychology |
Russian |
Full-time |
Diploma of Master's degree from Yanka Grodno State University and diploma of higher education in Kokand State University |
|
4 |
Karshi state University |
Republic of Uzbekistan |
4 years (2+2) |
16.1-25/20-8 12.05.2020 |
Faculty of Mathematics and Informatics / Applied Mathematics (scientific and industrial activities) |
Russian |
Full-time |
Diploma of Higher Education in Yanka Kupala State University of Grodno and diploma of higher education in Karshi state University |
|
5 |
Tashkent state university of law |
Republic of Uzbekistan |
4 years (3+1) |
16.1-25/20-10 08.07.2020 |
Faculty of Law / International Law |
Russian |
Full-time |
Diploma of Higher Education in Yanka Kupala State University of Grodno and diploma of higher education in Tashkent state university of law |
|
6 |
Tashkent state university of law |
Republic of Uzbekistan |
4 years (2+2) |
16.1-25/21-20 16.08.2021 |
Faculty of Law / International Law |
Russian |
Full-time |
Diploma of Higher Education in Yanka Kupala State University of Grodno and diploma of higher education in Tashkent state university of law |
|
7 |
Tashkent state university of law |
Republic of Uzbekistan |
5 years (2.5+2.5) |
Supplementary Agreement |
Faculty of Law / International Law |
Russian |
Part-time |
Diploma of Higher Education in Yanka Kupala State University of Grodno and diploma of higher education in Tashkent state university of law |
|
8 |
Tashkent institute of chemical technology |
Republic of Uzbekistan |
2 years (1+1) |
№ 5/02 05.07.2023 |
Faculty of Economics and Management / Management |
Russian |
Full-time |
Diploma of Higher Education in Yanka Kupala State University of Grodno and diploma of higher education in Tashkent institute of chemical technology |
|
9 |
Tashkent state University of transport |
Republic of Uzbekistan |
4 years (2+2) |
№ 16.1-25/24-4 01.05.2024 |
Faculty of Law / Law |
Russian |
Full-time |
Diploma of Higher Education in Yanka Kupala State University of Grodno and diploma of higher education in Tashkent state University of transport |
|
10 |
Tashkent state University of transport |
Republic of Uzbekistan |
5 years (3+2) |
Supplementary Agreement № 1 13.06.2024 |
Faculty of Law / Law |
Russian |
Part-time |
Diploma of Higher Education in Yanka Kupala State University of Grodno and diploma of higher education in Tashkent state University of transport |
|
11 |
Irkutsk state university |
Russian Federation |
2 years (1+1) |
08.06.2023 |
Faculty of Economics and Management / Economics |
Russian |
Full-time |
Diploma of Master's degree from Yanka Grodno State University and diploma from Irkutsk State University |
|
12 |
High school of Economics |
Russian Federation |
1 semester |
16.1-25/18-1 26.07.2018 |
Faculty of Law On the terms of parity, all the specialties of this faculty |
Russian |
Full-time |
Diploma of Higher Education in Yanka Kupala State University of Grodno High school of Economics Сertificate |
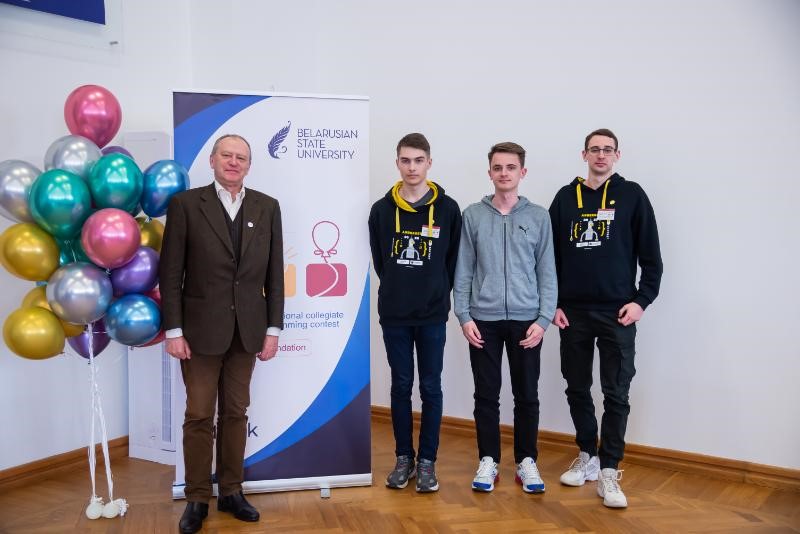
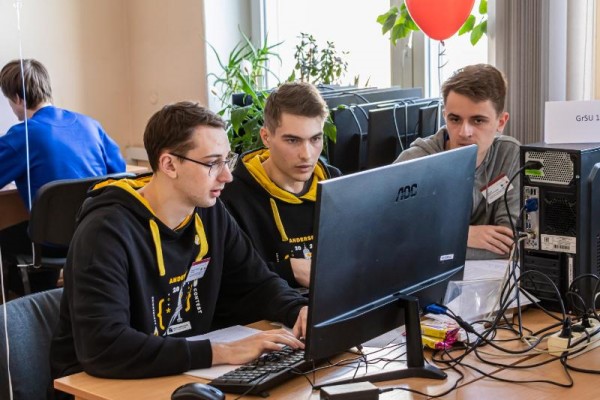
Students of Yanka Kupala State University became the prizewinners of the international programming competition

NERC Finals were held last week. More than 220 teams from universities of Belarus, Russia, Azerbaijan, Armenia, Georgia, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, and Uzbekistan took part in the championship. The competition was held in 4 cities (Saint-Petersburg, Barnaul, Almaty, Yerevan and Minsk) at the same time.
Yanka Kupala State University was represented by GrSU-1 and GrSU-2 teams, consisting of Vladilen Loktevich, Yury Sarosek, Nikolay Ignatenko and Andrey Hombak, Nikita Korenevsky, Nikolay Zdanchuk respectively.
Team GrSU-1 was the only team of all regional universities to get 3rd place.
Each team had one computer and five hours to solve 12 problems. The students had to create, introduce and prove the work of their algorithm and then write a program, using one of the programming languages. In order to win, the program must give only correct answers. Teams who had solved more problems won.
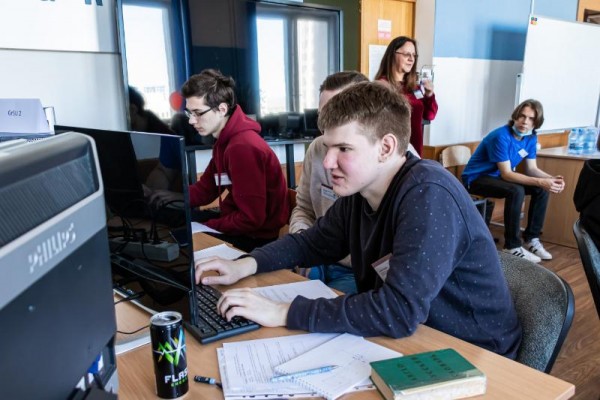


The team of the Mathematics and Informatics Faculty made it to the final of the International Data Analysis Olympiad (IDAO 2022)

Students of the Mathematics and Informatics Faculty Andrey Hombak, Dmitry Kulikov and Alexey Lelevich took part in the first qualifying round of the 5th International Data Analysis Olympiad (IDAO 2022) and made it to the final of the contest, which is to be held in Moscow.
The Olympiad is held by Yandex and the Faculty of Computer Sciences in Higher School of Economics (Russia). To make it through the round the students used their knowledge of neural networks to solve a problem connected with 2-D crystals of different configuration.
Our congratulations to the team! We wish you good luck in the final!
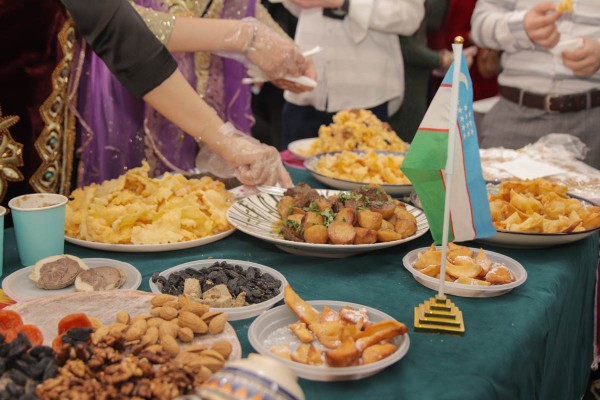
“Novruz Bayram” festival was held for the fifth time in Yanka Kupala State University of Grodno
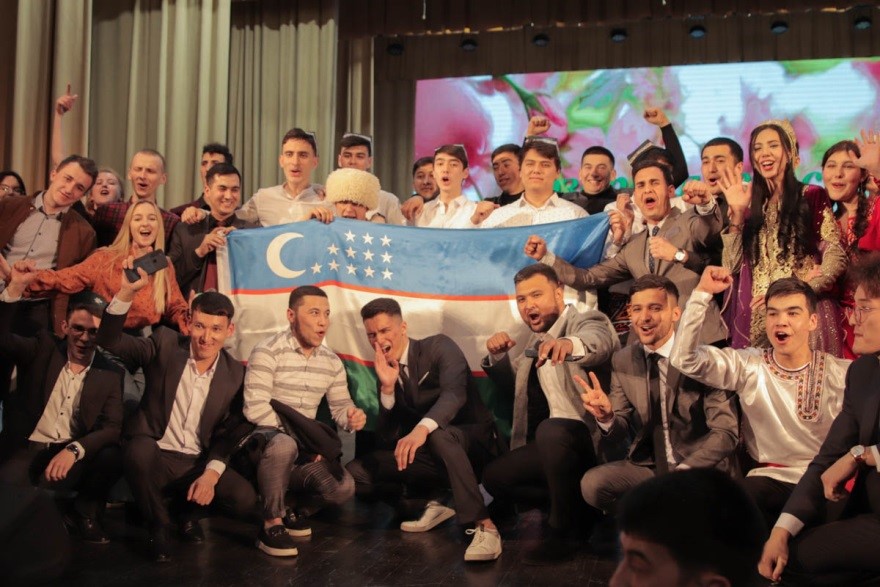

The holiday, symbolizing spring and new life among the Eastern peoples, was celebrated at the university on March 24-25.
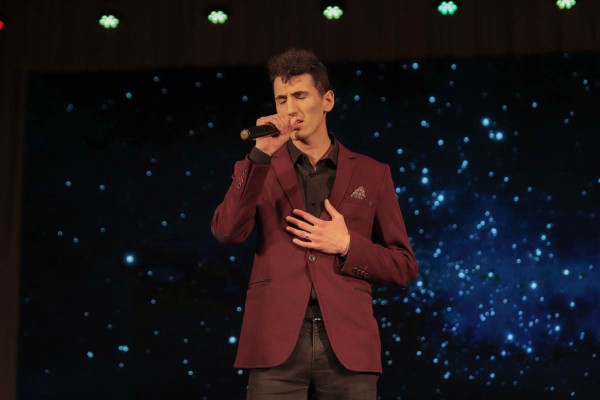
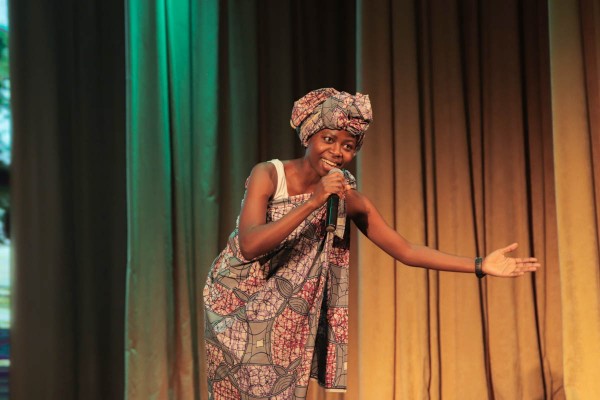
This year Novruz Bayram united the students of the Yanka Kupala State University of Grodno for the fifth time. The indoor football tournament, a fair-exhibition "Rainbow of Art", an amateur concert and an essay contest were held during the holiday.
The first Secretary of the Embassy of the Republic of Uzbekistan in the Republic of Belarus Azimjon Abdullayev and Consul of the Embassy of the Republic of Uzbekistan Hadjiakbar Vakhabov became the honored guests of the festival. They were given a tour of the university and organized a visit to the dormitories of the Yanka Kupala State University, so that representatives of the embassy could get acquainted with the daily life of students and university staff.
The participants and guests of the holiday were greeted by the Rector of the University Irina Kiturko.
- We try to make sure you feel at home in our country, even a thousand kilometers from your real one.
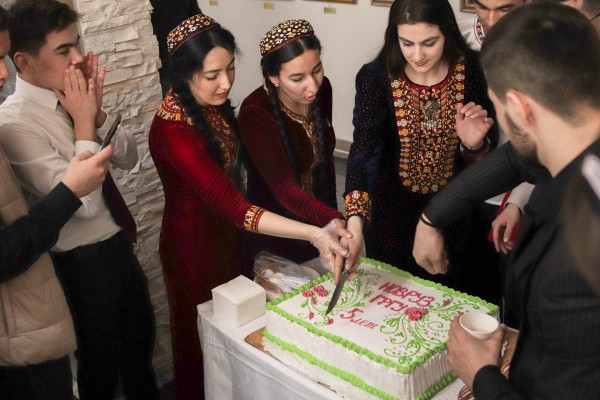
Irina Fedorovna thanked the students for supporting their national traditions and presented a cake to the participants of the festival.
Azimjon Abdullayev and Hadjiakbar Vakhabov addressed the organizers and guests of the holiday with a congratulatory word. They wished the students of Yanka Kupala State University family well-being, happiness and health.
As part of the anniversary celebration of Novruz Bayram, interactive platforms were organized where the guests of the event immersed themselves in the culture of other peoples. During the festival people could taste national dishes from Turkmenistan, Uzbekistan and Kazakhstan, learn Chinese and Iraqi calligraphy, appreciate the beauty of Oriental national costumes and hear authentic Chinese flute live.
Sports fans enjoyed the indoor football tournament, which ended with the victory of the team from Turkmenistan.
The festival ended with a concert, during which foreign students showed the audience their culture through creative performances. Vice-Rector for Academic Affairs Yuri Eduardovich Belykh addressed the guests and organizers of the holiday with congratulatory words.
As part of the concert, an award ceremony for the winners of the essay contest was held. The applications for participation in the contest were sent not only by Belarusians, but also representatives of countries such as Sri Lanka, Uzbekistan and Turkmenistan. In their essays the students decided to tell about their home countries and traditions connected with Novruz.
According to the results of the contest, Dinara Dzhumaniyazova was awarded a diploma of the first degree. The second and the third places were taken by Dulki Ruvanka Sirinivansa and Nyazik Nurberdieva respectively.